Swiss Tax Deductions
Every year, we have to pay our taxes. Each and every one of us has an obligation to file our tax returns correctly and within deadlines.
Faced with a tax return, the question arises. What is deductible from my taxes?
Let's take a look at the deductions you can use to reduce your tax bill. Happy reading!
Types of tax deductions in Switzerland
There are three types of tax deduction in Switzerland:
- 1. Organic deductions : They are directly linked to taxable income.
- 2. General deductions : They are linked to the taxpayer's lifestyle
- 3. Social deductions: They take into account the taxpayer's family situation
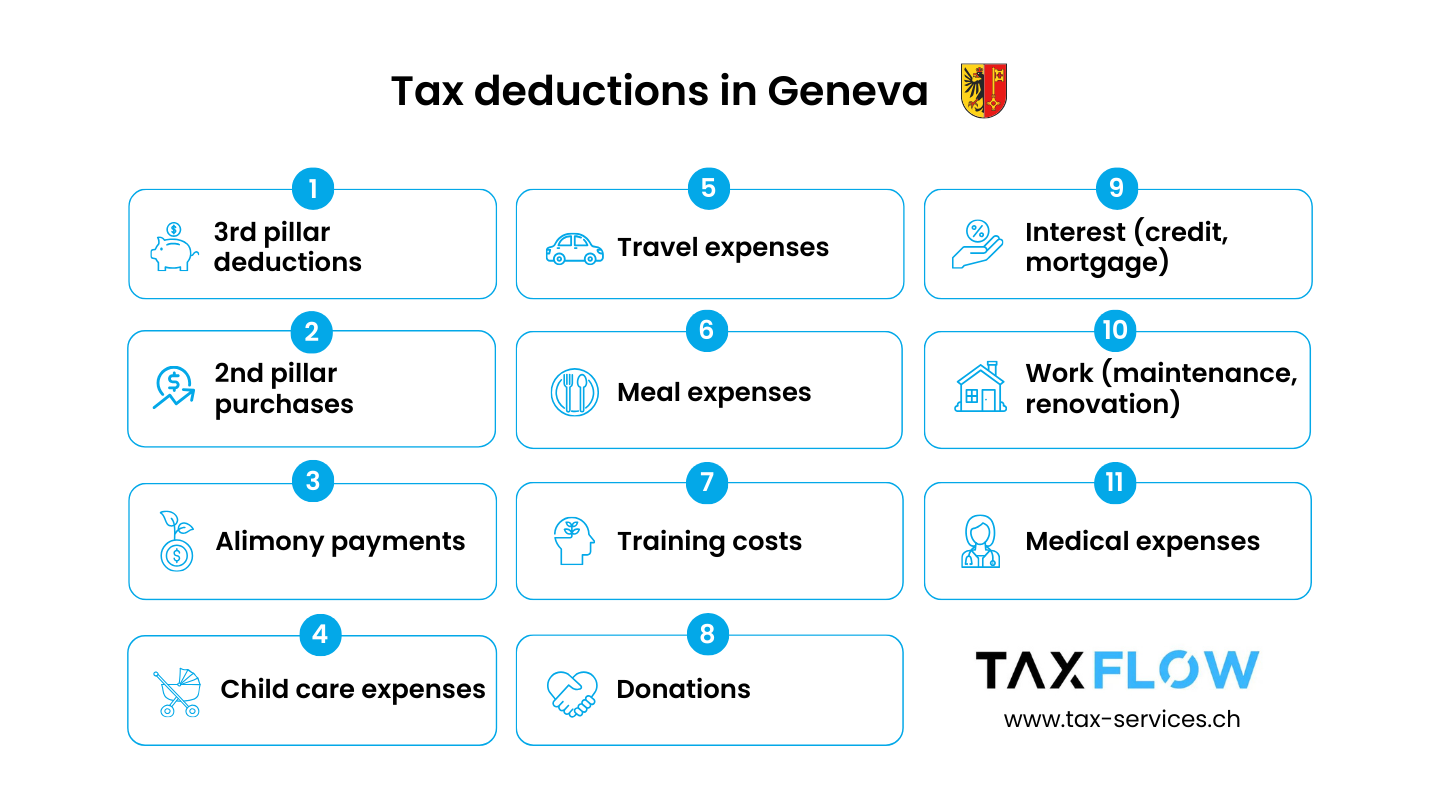
11 tax allowances in the canton of Geneva
1. 3rd pillar deductions
Deduction from 3rd pillar A
It may be worth taking out a 3rd pillar to reduce your tax bill and improve your situation once you retire.
Le 3nd pilier A est lié à l’âge de la retraite et rattaché aux conditions du 2nd pilier pour le retrait des fonds. Celui-ci est déductible à hauteur de 7’258 CHF en 2025 (7’056 CHF en 2024).
Pour les freelancers qui ne sont pas affiliés à un 2nd pilier, la déduction peut aller jusqu’à 20% du revenu réalisé, mais au maximum jusqu’à 36’288 CHF en 2025 (35’280 CHF en 2024).
Deduction from 3rd pillar B
Les primes du 3ème pilier B sont déductibles jusqu’à 3’348 CHF pour les couples and 2’232 CHF pour les célibataires, veufs, divorcés ou séparés.
These limits are doubled if the taxpayers, whether in a couple or not, are not affiliated to a pension fund. If only one of the spouses is affiliated, the limit for the couple increases to 1.5 times the initial value.
The deduction is increased by 900 CHF for each dependent. For a single, widowed, divorced or separated taxpayer living alone with dependent children and not affiliated to a provident scheme, the deduction doubles. When, in a couple, only one of the spouses is affiliated to a provident scheme, the deduction for family expenses is 1'350 CHF.
2. 2nd pillar purchases
Your salary has evolved, your situation has changed and you've been able to save a little money. It may be worthwhile checking with your pension fund to see whether a purchase is possible. The LPP buy-back is 100% deductible from your income.
3. Alimony payments
Maintenance contributions made to your ex-spouse following a divorce or de facto separation, as well as payments to your ex-spouse for minor children, are deductible.
Pensions for adult children are not deductible.
4. Deductions for childcare costs
Le canton de Genève a pris la décision de considérer les camps comme des frais de garde déductibles, une déduction de 250 CHF par camps et semaine est possible pour tous les parents genevois et cela à partir de l’année fiscale 2022.
Les frais de garde sont plafonnés à 25,000 CHF par enfant de moins de 14 ans à charge.
A social deduction of 6,500 CHF is granted for each child for whom the taxpayer provides maintenance. Provided that:
- The child is under 18
- The child is aged between 18 and 25 and in education or apprenticeship
5. Travel expenses
Les frais de transport nécessaires entre le domicile et le lieu de travail sont déductibles et plafonnés à 529 CHF en 2024 (507 en 2023) à Genève.
Au niveau fédéral, vous pouvez déduire jusqu’à 3’200 CHF fonction de la distance parcourue entre votre travail et votre domicile.
6. Meal expenses
The meal expenses are deductible up to CHF3,200 per year provided that:
- The employee cannot have meals at home
(long distance/irregular or night shifts) - The employer does not pay for the meal
If the employer contributes to the reduction of the burden (case G) by means other than cash, for example by providing a canteen or restaurant for the employees. This deduction is halved (max. 1,600 CHF).
7. Training costs
Are tax-deductible expenses, your training costs and further training for professional purposes, including retraining costs, up to max. 12’640 CHF en 2024 (12’140 CHF en 2023) par année, à condition de :
- Hold an upper-secondary level diploma
- Are aged 20 or over, and are following a course of study leading to a diploma other than a first upper-secondary level diploma.
8. Donation deductions
Donations to legal entities domiciled in Switzerland and pursuing a tax-exempt charitable purpose, as well as donations to the Confederation, cantons, municipalities and public institutions, are deductible up to a maximum of 20% of net income.
9. Interest deductions
Interest on consumer loans, mortgages or private debts is deductible.
Please note that interest on building loans is not deductible.
Interest is deductible to the extent of the return on assets plus CHF 50,000.
10. Tax deductions for construction work
Maintenance/renovation work
All work carried out to maintain the value of the property is considered maintenance.
Energy-saving work
Work aimed at saving energy is deductible. (Insulation, energy monitoring, photovoltaic panels, replacement of certain appliances provided they are part of the building).
Management and other actual costs
Management costs may be deducted provided they have been incurred by third parties. These include postage, telephone, advertisements, printed matter, legal proceedings, court costs and management fees.
11. Medical expenses
Les frais liés à la santé sont déductibles, en font partie la prime d’assurance maladie et assurance accident.
Les frais effectifs liés à la maladie ou à un accident que le contribuable doit supporter sont également déductibles à conditions que les frais dépassent 0.5% (ICC) et 5% (IFD) du revenu net.
Example of deductible expenses :
- Medication: Medicines that are not covered by insurance can be deducted provided they have been prescribed by an approved doctor or naturopath.
- Dental expenses : Dental expenses, orthodontic treatments, surgeries, hygiene are eligible and considered as medical expenses. On the other hand, expenses related to purely cosmetic purposes are not deductible.
- Natural medicine: Expenses related to alternative medicine treatments are deductible provided they are prescribed by a registered naturopath. No need to have a prescription from a conventional doctor.
- Frais de régime alimentaire : En cas de nécessité vitale de suivre un régime particulier, notamment en cas de diabète. Une déduction forfaitaire de 2'500 CHF est admise sans besoin d’apporter ou conserver les justificatifs.
Tax Advice
There are many deductions and, above all, they are subject to countless conditions. We can help you draw up your Geneva tax return, so that you don't forget anything and can claim all the deductions to which you are entitled.
Our chartered tax accountants will answer your questions and help you if your situation changes (birth, death, acquisition of a property, etc.).





